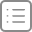
查看AAPT命令格式
看到这里,有很多开发者可能会问:笔者是如何记得这么多的指令和它们的参数的?答案就是——其实笔者也不记得。
那么笔者是如何获取这些指令的使用方法的呢?相信经常使用Linux系统的开发者应该很清楚,通常终端程序都会有帮助,AAPT工具同样是这样。在终端下直接执行./aapt指令就可以获取所有的使用方法,显示结果如下所示。
- ➜ 23.0.2 ./aapt
- Android Asset Packaging Tool
- Usage:
- aapt l[ist] [-v] [-a] file.{zip,jar,apk}
- List contents of Zip-compatible archive.
- aapt d[ump] [--values] [--include-meta-data] WHAT file.{apk} [asset [asset ...]]
- strings Print the contents of the resource table string pool in the APK.
- badging Print the label and icon for the app declared in APK.
- permissions Print the permissions from the APK.
- resources Print the resource table from the APK.
- configurations Print the configurations in the APK.
- xmltree Print the compiled xmls in the given assets.
- xmlstrings Print the strings of the given compiled xml assets.
- aapt p[ackage] [-d][-f][-m][-u][-v][-x][-z][-M AndroidManifest.xml] \
- [-0 extension [-0 extension ...]] [-g tolerance] [-j jarfile] \
- [--debug-mode] [--min-sdk-version VAL] [--target-sdk-version VAL] \
- [--app-version VAL] [--app-version-name TEXT] [--custom-package VAL] \
- [--rename-manifest-package PACKAGE] \
- [--rename-instrumentation-target-package PACKAGE] \
- [--utf16] [--auto-add-overlay] \
- [--max-res-version VAL] \
- [-I base-package [-I base-package ...]] \
- [-A asset-source-dir] [-G class-list-file] [-P public-definitions-file] \
- [-S resource-sources [-S resource-sources ...]] \
- [-F apk-file] [-J R-file-dir] \
- [--product product1,product2,...] \
- [-c CONFIGS] [--preferred-density DENSITY] \
- [--split CONFIGS [--split CONFIGS]] \
- [--feature-of package [--feature-after package]] \
- [raw-files-dir [raw-files-dir] ...] \
- [--output-text-symbols DIR]
- Package the android resources. It will read assets and resources that are
- supplied with the -M -A -S or raw-files-dir arguments. The -J -P -F and -R
- options control which files are output.
- aapt r[emove] [-v] file.{zip,jar,apk} file1 [file2 ...]
- Delete specified files from Zip-compatible archive.
- aapt a[dd] [-v] file.{zip,jar,apk} file1 [file2 ...]
- Add specified files to Zip-compatible archive.
- aapt c[runch] [-v] -S resource-sources ... -C output-folder ...
- Do PNG preprocessing on one or several resource folders
- and store the results in the output folder.
- aapt s[ingleCrunch] [-v] -i input-file -o outputfile
- Do PNG preprocessing on a single file.
- aapt v[ersion]
- Print program version.
- Modifiers:
- -a print Android-specific data (resources, manifest) when listing
- -c specify which configurations to include. The default is all
- configurations. The value of the parameter should be a comma
- separated list of configuration values. Locales should be specified
- as either a language or language-region pair. Some examples:
- en
- port,en
- port,land,en_US
- -d one or more device assets to include, separated by commas
- -f force overwrite of existing files
- -g specify a pixel tolerance to force images to grayscale, default 0
- -j specify a jar or zip file containing classes to include
- -k junk path of file(s) added
- -m make package directories under location specified by -J
- -u update existing packages (add new, replace older, remove deleted files)
- -v verbose output
- -x create extending (non-application) resource IDs
- -z require localization of resource attributes marked with
- localization="suggested"
- -A additional directory in which to find raw asset files
- -G A file to output proguard options into.
- -F specify the apk file to output
- -I add an existing package to base include set
- -J specify where to output R.java resource constant definitions
- -M specify full path to AndroidManifest.xml to include in zip
- -P specify where to output public resource definitions
- -S directory in which to find resources. Multiple directories will be scanned
- and the first match found (left to right) will take precedence.
- -0 specifies an additional extension for which such files will not
- be stored compressed in the .apk. An empty string means to not
- compress any files at all.
- --debug-mode
- inserts android:debuggable="true" in to the application node of the
- manifest, making the application debuggable even on production devices.
- --include-meta-data
- when used with "dump badging" also includes meta-data tags.
- --pseudo-localize
- generate resources for pseudo-locales (en-XA and ar-XB).
- --min-sdk-version
- inserts android:minSdkVersion in to manifest. If the version is 7 or
- higher, the default encoding for resources will be in UTF-8.
- --target-sdk-version
- inserts android:targetSdkVersion in to manifest.
- --max-res-version
- ignores versioned resource directories above the given value.
- --values
- when used with "dump resources" also includes resource values.
- --version-code
- inserts android:versionCode in to manifest.
- --version-name
- inserts android:versionName in to manifest.
- --replace-version
- If --version-code and/or --version-name are specified, these
- values will replace any value already in the manifest. By
- default, nothing is changed if the manifest already defines
- these attributes.
- --custom-package
- generates R.java into a different package.
- --extra-packages
- generate R.java for libraries. Separate libraries with ':'.
- --generate-dependencies
- generate dependency files in the same directories for R.java and resource package
- --auto-add-overlay
- Automatically add resources that are only in overlays.
- --preferred-density
- Specifies a preference for a particular density. Resources that do not
- match this density and have variants that are a closer match are removed.
- --split
- Builds a separate split APK for the configurations listed. This can
- be loaded alongside the base APK at runtime.
- --feature-of
- Builds a split APK that is a feature of the apk specified here. Resources
- in the base APK can be referenced from the the feature APK.
- --feature-after
- An app can have multiple Feature Split APKs which must be totally ordered.
- If --feature-of is specified, this flag specifies which Feature Split APK
- comes before this one. The first Feature Split APK should not define
- anything here.
- --rename-manifest-package
- Rewrite the manifest so that its package name is the package name
- given here. Relative class names (for example .Foo) will be
- changed to absolute names with the old package so that the code
- does not need to change.
- --rename-instrumentation-target-package
- Rewrite the manifest so that all of its instrumentation
- components target the given package. Useful when used in
- conjunction with --rename-manifest-package to fix tests against
- a package that has been renamed.
- --product
- Specifies which variant to choose for strings that have
- product variants
- --utf16
- changes default encoding for resources to UTF-16. Only useful when API
- level is set to 7 or higher where the default encoding is UTF-8.
- --non-constant-id
- Make the resources ID non constant. This is required to make an R java class
- that does not contain the final value but is used to make reusable compiled
- libraries that need to access resources.
- --shared-lib
- Make a shared library resource package that can be loaded by an application
- at runtime to access the libraries resources. Implies --non-constant-id.
- --error-on-failed-insert
- Forces aapt to return an error if it fails to insert values into the manifest
- with --debug-mode, --min-sdk-version, --target-sdk-version --version-code
- and --version-name.
- Insertion typically fails if the manifest already defines the attribute.
- --error-on-missing-config-entry
- Forces aapt to return an error if it fails to find an entry for a configuration.
- --output-text-symbols
- Generates a text file containing the resource symbols of the R class in the
- specified folder.
- --ignore-assets
- Assets to be ignored. Default pattern is:
- !.svn:!.git:!.ds_store:!*.scc:.*:<dir>_*:!CVS:!thumbs.db:!picasa.ini:!*~
- --skip-symbols-without-default-localization
- Prevents symbols from being generated for strings that do not have a default
- localization
- --no-version-vectors
- Do not automatically generate versioned copies of vector XML resources.
这份文档解释了AAPT所能够使用的各种指令。如果开发者在使用过程中不记得某些指令的参数或者使用方法,那么直接使用这个指令就可以获取到你想要的内容了。