21.5 Objective-C版本的计算器
前面的小节中我们介绍了纯Swift实现的iPhone计算器,这一节我们介绍Objective-C版本的iPhone计算器。由于本书并不是介绍Objective-C语言的书,因此本章我们假定广大读者对Objective-C语言是熟悉的。介绍Objective-C版本的主要目的是比较对于相同的一个应用,使用两种不同的语言(Objective-C和Swift)开发实现有哪些差别。Objective-C版本的iPhone计算器源代码随书一起发布给大家,这里不再详细介绍实现过程。
21.5.1 Xcode工程文件结构比较
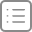
我们使用Xcode打开两个工程,Xcode工程文件结构如图21-34所示,左图为Swift版本,右图为Objective-C版本。

图 21-34 工程文件结构
从图中可见,Objective-C中有.h文件和.m(或.mm)文件,而Swift中只需要一个文件.swift,不需要h文件。至于其他的文件,如资源文件、配置文件和故事板文件(Main.storyboard)都没有区别,甚至在打开故事板Main.storyboard进行界面设计时也都是一样的。
21.5.2 表示层比较
表示层主要是视图控制器ViewController,Objective-C版本中的ViewController.h文件代码如下:
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>#import "CalcLogic.h"@interface ViewController : UIViewController{CalcLogic *logic; ①}@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UILabel *mainLabel; ②- (IBAction)operandPressed:(id)sender; ③- (IBAction)equalsPressed:(id)sender;- (IBAction)clearPressed:(id)sender;- (IBAction)decimalPressed:(id)sender;- (IBAction)numberButtonPressed:(id)sender;@end
Objective-C中的h文件用来声明类和类中成员,其中成员变量是在{}之间定义的,代码第①行定义成员变量logic。第②行代码是定义属性,Objective-C属性类似于Swift中的计算属性。第③行代码是声明成员方法,这些方法具体的属性要在m或mm文件中实现。
Objective-C版本中ViewController.m文件代码如下:
#import "ViewController.h"@interface ViewController ()@end@implementation ViewController- (void)viewDidLoad {[super viewDidLoad];self.mainLabel.text = @"0";logic = [[CalcLogic alloc] init];}- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];}- (IBAction)operandPressed:(id)sender {UIButton* btn = (UIButton*)sender;self.mainLabel.text = [logic calculateByTag:btn.tag withMainLabelString:self.mainLabel.text];}- (IBAction)equalsPressed:(id)sender {UIButton* btn = (UIButton*)sender;self.mainLabel.text = [logic calculateByTag:btn.tag withMainLabelString:self.mainLabel.text];}- (IBAction)clearPressed:(id)sender {self.mainLabel.text = @"0";[logic clear];}- (IBAction)decimalPressed:(id)sender {if ( [logic doesStringContainDecimal:self.mainLabel.text] == FALSE) {NSString *s = [self.mainLabel.text stringByAppendingString:@"."];self.mainLabel.text = s;}}- (IBAction)numberButtonPressed:(id)sender {UIButton* btn = (UIButton*)sender;self.mainLabel.text = [logic updateMainLabelStringByNumberTag:btn.tagwithMainLabelString:self.mainLabel.text];}@end
我们可以比较一下上述代码与Swift中代码的区别,这里不再赘述。
21.5.3 业务逻辑层比较
Objective-C版本中的CalcLogic.h文件代码如下:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>typedef enum { ①Plus = 200, Minus, Multiply, Divide,Default = 0} Operator; ②@interface CalcLogic : NSObject ③{//保存上一次的值double lastRetainValue;//最近一次选择的操作符(加、减、乘、除)Opertor opr;//临时保存MainLabel内容,为true时,输入数字MainLabel内容被清为0BOOL isMainLabelTextTemporary;}//构造方法-(id) init; ④-(void)clear;-(NSString*)updateMainLabelStringByNumberTag:(int) tagwithMainLabelString:(NSString*)mainLabelString;-(BOOL)doesStringContainDecimal:(NSString*)string;-(NSString*)calculateByTag:(int) tagwithMainLabelString:(NSString*)mainLabelString;@end
我们在h文件中除了声明CalcLogic类之外,还定义了枚举Operand,代码第①~②行是定义枚举Operand类型,Objective-C中的枚举Operand与Swift枚举有很大的差别。Objective-C中的枚举成员值只能是整数类型。
第③行代码是声明CalcLogic类,它继承了NSObject类,在Objective-C中所有类的根类都是NSObject类。第④行代码是声明构造函数init(),它的作用相当于Swift中的构造器。它的命名一般都是以init开头,返回值是本身类型的指针,而Swift中的构造器没有返回值。
Objective-C版本中的CalcLogic.m文件代码如下:
#import "CalcLogic.h"@implementation CalcLogic//构造方法-(id) init{NSLog(@"CalcLogic init");self = [super init]; ①if (self) { ②lastRetainValue = 0.0;isMainLabelTextTemporary = FALSE;opr = Default;}return self; ③}-(void)clear{lastRetainValue = 0.0;isMainLabelTextTemporary = FALSE;opr = Default;}-(NSString*)updateMainLabelStringByNumberTag:(int) tagwithMainLabelString:(NSString*)mainLabelString{NSString* string = mainLabelString;if (isMainLabelTextTemporary) {string = @"0";isMainLabelTextTemporary = FALSE;}int optNumber = tag - 100;//把String转为doubledouble mainLabelDouble = string.doubleValue;if (mainLabelDouble == 0&& [self doesStringContainDecimal: string] == false) {NSString *strOptNumber = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%i", optNumber];return strOptNumber;}NSString *resultString = [string stringByAppendingFormat:@"%i", optNumber];return resultString;}-(BOOL)doesStringContainDecimal:(NSString*)string{NSString *searchForDecimal = @".";NSRange range = [string rangeOfString:searchForDecimal];if (range.location != NSNotFound)return YES;return NO;}-(NSString*)calculateByTag:(int) tagwithMainLabelString:(NSString*)mainLabelString{//把String转为为doubledouble currentValue = mainLabelString.doubleValue;switch (opr) { ④case Plus:lastRetainValue += currentValue;break; ⑤case Minus:lastRetainValue -= currentValue;break;case Multiply:lastRetainValue *= currentValue;break;case Divide:if (currentValue != 0) {lastRetainValue /= currentValue;} else {opr = Default;isMainLabelTextTemporary = TRUE ;return @"错误";}break;Default:lastRetainValue = currentValue;}//记录当前操作符,下次计算时使用opr = tag;NSString* resultString = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%g", lastRetainValue];isMainLabelTextTemporary = TRUE ;return resultString;}@end
上述代码程序结构上与Swift版一样,但在语法上有很大区别,代码第①行self = [super init]语句是先构造父类实例,然后在第②行判断是否成功,如果成功再初始化成员变量。第③行返回自身对象的指针,这就是Objective-C语言的构造过程,要比Swift繁琐。
还有代码第④行使用switch语句。对于switch语句,Objective-C与Swift有很大的差别,Objective-C的switch语句的每一个分支都需要加break,否则就会贯穿;而Swift默认每个分支都有break。